After-tax Rate Of Return
The term after-tax rate of return calculates an investor’s net return after income taxes. The calculation is used by many businesses and investors to determine their real earnings. Another way of looking at it is to determine the profit realized on an investment after taxes are subtracted from it.
The resulting after-tax rate of return can be expressed as a ratio or nominally. During the after-tax rate of return calculation, the values included should only be from the reported period, not outside of it.
Understanding the After-Tax Rate of Return
For real estate investors, being able to calculate the after-tax rate of return is essential. Through this calculation, they can understand which is the actual profit that the investment generates.
Regardless of the type of investment that attracts any particular investor, profit is the most attractive element. Whether it is bonds, stocks, real estate, or other, the ability to generate profit makes one investment opportunity more attractive than another.
To understand why the after-tax rate of return is important for investors, we must understand how investors choose their investments. An investor will overlook investments that generate higher before-tax returns and decide to invest in those that generate lower before-tax returns if the after-tax rate of return is higher. They do this because an investment with a higher after-tax rate of return is an investment with a higher profit, while high before-tax rates of return can mean a lower after-tax rate of return. This situation is often applied to high tax bracket investors, but the after-tax rate of return formula can be applied to any kind of investment.
The After-Tax Rate of Return Formula
The formula itself is straightforward, but gathering the necessary information can be a complicated task. Before you begin the calculation, you have to figure out how taxes are applied to your investment. The only information included in the after-tax rate of return formula should only include the income received and costs paid during the reporting period for the rate of return. The same should be done for the tax rate by considering how the tax rate is applied to the investment for which the after-tax rate of return is calculated.
The basic formula for calculating the after-tax rate of return is:
ATRR = RoR x (1- Tax Rate)
Where:
ATRR is the After-Tax Rate of Return
RoR is the Rate of Return
Tax Rate is the tax rate applied to the investment.
This formula can be applied to calculate the after-tax rate of return for real estate investments and other less complicated investments.
The formula for calculating the after-tax rate of return for stock investment is:
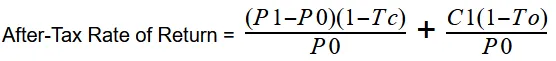
Where:
P0 is the buy stock value.
P1 is the sell stock value after one year.
C1 is the dividend.
Tc is the long-term capital gains tax rate.
To is the income tax rate.
This formula accounts for how long-term capital gains are taxed and how income dividends are affected by the income tax rate. Those are some of the reasons why this variant of the formula is much more complicated.
How to Calculate After-Tax Rate of Return?
We have the scenario where John has bought a house for $300,000, and he sells it for $380,000 while having a tax rate of $4,000 annually for the property or 1%. First, he needs to discover the rate of return on investment.
RoR = [(Current value - Initial Value) : Initial Value] x 100
RoR = [($380,000 - $300,000) : $300,000] x 100
RoR = 0.2666 x 100
RoR = 26%
With the rate of return at his disposal, he can determine the After-Tax Rate of Return:
ATRR = RoR x (1 - Tax Rate)
ATRR = 26% x (1 - 4%)
ATRR = 24%
Popular Real Estate Terms
Are you speculating what a spec house means? (sorry for the lousy pun) The textbook spec (or speculative) house definition is “one built on an experimental basis, without an order ...
Regularly, subsequent means something which occurs at a later date. In other words, a subsequent event follows a prior occurrence. For example, new circumstances arise after a contract is ...
The number of units currently occupied in a facility, neighborhood, or city, stated as a percentage of total capacity. For example, a hotel has 80 rooms available for guests. Its average ...
The term “property title” is relatively common and often used in the real estate industry, which is why it’s useful to know what it really means. While the term itself is ...
Drilled well where water rises through the opening because of naturally occurring water pressure. ...
Condensed appraisal report covering the major items. ...
When talking about the open space ratio we are referring to a term that is used in zoning laws and regulations. The open space ratio is a term used to measure open space on a developed land ...
Method of describing a real estate property offering by a developer in lieu of a prospectus. ...
Organizational governing group. Either an appointed or elected body overseeing the management of an organization and rendering advice on current issues. Members are legally responsible for ...
Have a question or comment?
We're here to help.