Annuity Factor
The annuity factor definition is the use of a financial method that shows the value, present or future, of an amount when it is multiplied by a periodic amount. The calculation of an annuity factor requires the number of years involved, or the periodic amount, and the percentage rate applicable. The most often used for annuity factors are investments with either or both an annual payment or return. Typical examples of annuity factors being applied are savings accounts, certain types of insurances, or retirement savings plans.
The annuity factor meaning is a particular type of accumulating discount factor used to determine the present or future value of annuities, as well as equated installments. Another name for annuity factors is the annuity formula, and we’ll get into that momentarily.
The Present Value Annuity Factor
The present value annuity factor allows you to determine the amount of money required at the present time in order to result in a future series of payments assuming a fixed interest rate is applied.
In order to reach the present value annuity factor, a formula is used that discounts a future value amount to the present value amount through the use of the applicable interest rate. The period of time during which the investment will last is also taken into account to reach the correct value.
The Present Value Annuity Formula
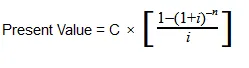
With:
C=cash flow per period
i = interest rate
n = number of payments
The Future Value Annuity Factor
The future value annuity factor gives access to the final return value of a series of regular investments taking into account their worth at a future time, usually at the end of the investing period, assuming that a fixed interest rate is applied.
To reach the future value annuity factor, the formula above is slightly altered in order to add the values collected over the years by also accounting for the set interest rate.
The Future Value Annuity Factor
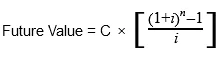
With:
C=cash flow per period
i = interest rate
n = number of payments
Applying the Annuity Factor formulas:
Considering an investment with an annual $2,000 payment over the course of five years at an interest rate of 5%, let’s see what the present and future value would be.
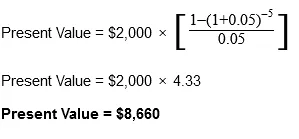
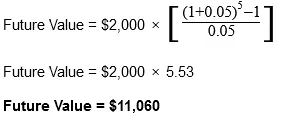
The previous formulas can help you determine the present and future values of ordinary annuities. While the math might seem complicated, there are financial calculators online that can help you out with the correct inputs and data.
Popular Real Estate Terms
Court action to order a compulsory sale of real estate owned jointly between two or more owners. A partition action divides the proceeds of a real estate sale among the joint owners rather ...
mortgage being reduced through periodic principal and interest payments. ...
Section of the Internal Revenue Code relating to depreciation. Capital improvements made to real property are depreciable. ...
To create an encumbrance. ...
Expected period that property will provide benefits. It is typically less than physical life of the property because the property continues to have physical life regardless of inefficiency ...
To obtain the right through authorization to act as a legal representative and agent for another. ...
Member Of the American Institute of Real Estate Appraisers. ...
(1) Government seizes private property, but does not provide fair and reasonable compensation for it. (2) Property is seized and the owners rights abolished because of a legal violation. ...
The phrase used for the period in which the escrow agent communicates to both the buyer and the seller as to what documents or moneys have to be deposited with the escrow agent to satisfy ...
Have a question or comment?
We're here to help.