Effective Interest Rate
The term effective interest rate is the actual return from a savings account or any investment where you pay interest when considering the effects of compounding costs over time. Through an effective interest rate, you can fully and correctly determine the real percentage rate that you own on a loan’s interest, a credit card, or any other debt type.
An effective interest rate is also referred to as an effective annual interest rate, the annual equivalent rate, or the effective rate.
The Effective Interest Rate Formula:
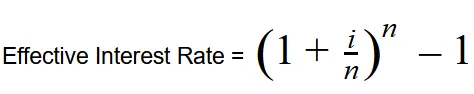
With:
i = Nominal Interest Rate
n = Number of periods
What does the Effective Interest Rate Mean?
When you look at loans, the way through which they are advertised will give you two types of information. Firstly, we’ll have the nominal interest rate, which doesn’t consider the effects compounding interest or fees have on the financial product. Secondly, and the one we focus on now, the effective interest rate, which gives you the real return paid on savings of the actual cost of a loan because it does take into account the effect fees and compounding interest have on the financial product.
For that exact reason, knowing and understanding what the effective interest rate means is important. Through a proper understanding of the effective interest rate, you can compare offers more accurately to make an informed decision based on the result.
How to Find the Effective Interest Rate?
To adequately explain how to find the effective interest rate from any financial product’s promotional information, we will look at two examples. Firstly, we’ll have Loan A that has a 5% interest rate that’s compounded monthly. Secondly, we’ll have Loan B with a 5.1% interest rate that’s compounded bi-annually.
Both of these loans are advertised with their nominal interest rate. Remember, this is the one that doesn’t take into account the effects fees and compounding interest has on the loan. To calculate the effective interest rate, we’ll use the formula shown above.
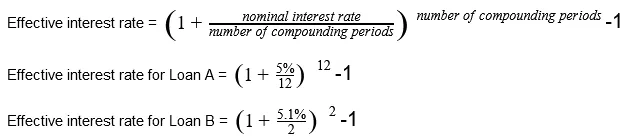
While the nominal interest rate for Loan A is smaller than that of Loan B’s, the effective interest rate from Loan B is lower than that of Loan A’s. This occurs because Loan B has fewer compounding times over the course of a year.
Popular Real Estate Terms
Personal income minus personal income tax payments and other government deductions. It is the personal income available for people to spend or save; also called take-home pay. It may be a ...
Civil rights acts passed by the U.S. Congress includes those of 1866, 1870, 1871, 1875, 1964, and 1968. The first two acts gave blacks the rights to be treated as citizens in legal actions, ...
Appraisal performed in accordance with the National Housing Act to determine the resale value of vacant or improved property in an urban area to be or under development. The renewal ...
Organization that manages the relocation of the employees of client companies from one area of the country to another. A relocation service will manage home sales and purchases in another ...
Housing where affirmative action is actively pursued encouraging people of all races, nationalities, and religions to purchase or rent the facilities. ...
Canceling, nullifying, terminating, or dishonoring a contractual obligation. The Truth-in-Lending Act provides the right of rescission whereby a person can annul a contract without ...
Title granted to those having expertise in valuing homes by the American Institute of Real Estate Appraisers. ...
Any of a number of types of covenants agreeing to do or not to do something that is attached to the title and is passed form one owner to the next. See also covenant running with the land. ...
Company formed for the purpose of owning securities of one or more real estate corporations and assuming control over their practices and management. The other corporations are generally ...
Have a question or comment?
We're here to help.